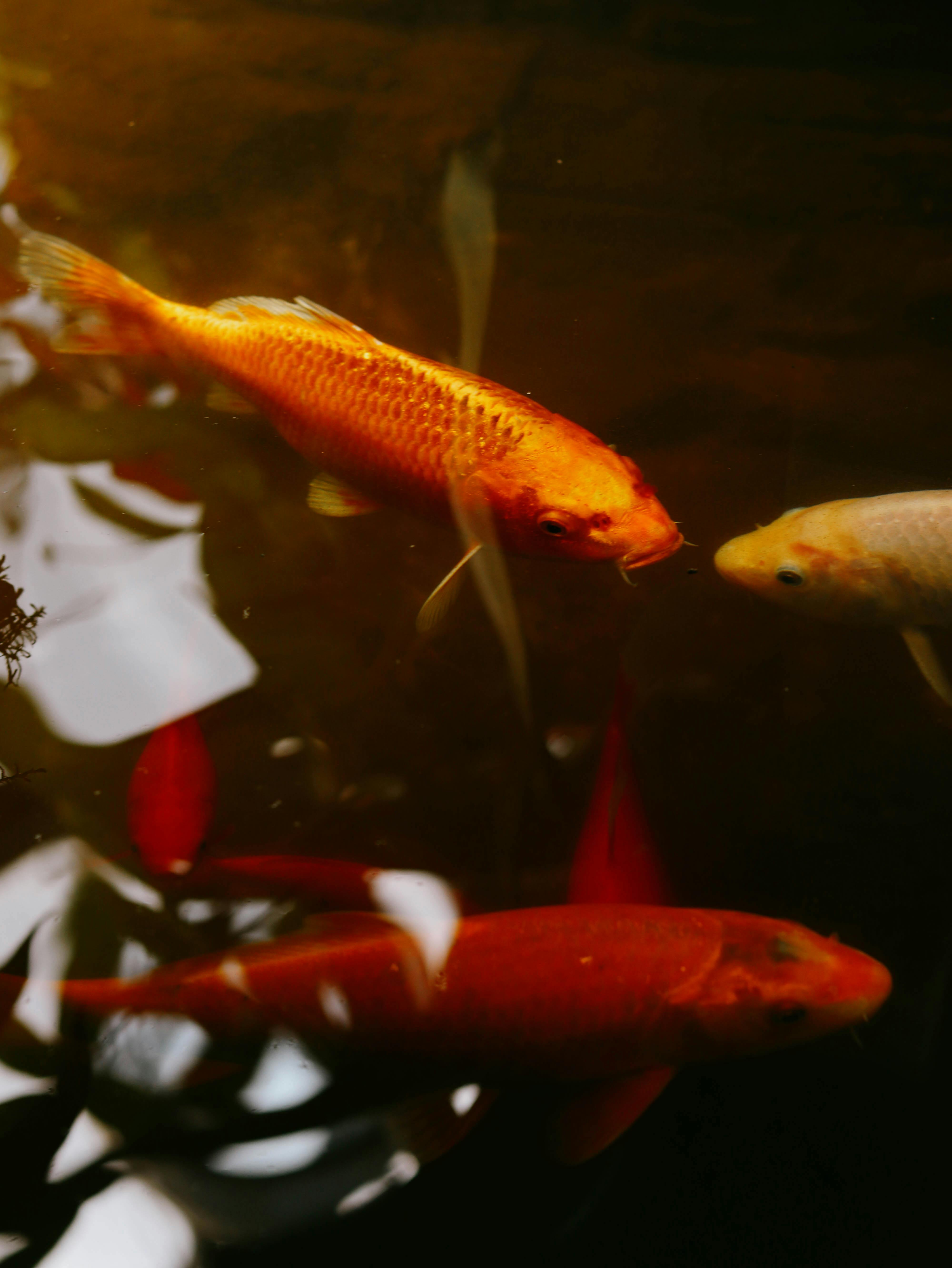
Top 5 Differences Between Male and Female Guppies Understanding Guppy Sexual Dimorphism Guppies, popular among aquarium enthusiasts, showcase remarkable differences between males and females, driven largely by sexual dimorphism. Male guppies (Poecilia reticulata) feature vibrant colors and intricate patterns that serve not just for aesthetics, but also play crucial roles in attracting mates. The bright hues and extended fins are often characteristics...
Smart Ways to Choose Better Female Bettas for Sale in 2025 Choosing the right female bettas requires more than just random selection; it involves understanding the various aspects of betta fish care and their specific needs. In 2025, potential owners are increasingly interested in acquiring healthy and vibrant bettas that complement their aquarium environments. Female bettas, known for their stunning colors...
Smart Ways to Use a 30 Gallon Terrarium for Better Growth Introduction to Crafting a 30 Gallon Terrarium Creating a 30-gallon terrarium opens up exciting possibilities for indoor gardening while enhancing your living space's aesthetic. Terrariums are more than just decorative items; they offer a mini-ecosystem where plants, moisture, and light come together harmoniously, promoting better growth and healthier plants. With the...
Effective Ways to Choose the Right Guppy Tank Size for 2025 Setting up a guppy tank is an exciting venture for both novice and experienced aquarists. Guppies, known for their vibrant colors and lively nature, require specific tank sizes to thrive in a healthy environment. Knowing the ideal tank size for guppies is crucial not only for their wellbeing but also...
Essential Guide to Big Fish Aquarium Care in 2025 As aquarists navigate the expansive universe of aquarium keeping, the year 2025 marks a significant evolution in the approaches to big fish aquarium care. With advancements in technology and an increased understanding of aquatic ecosystems, ensuring the proper maintenance and health of large aquarium setups becomes paramount. From selecting the best aquarium...
Best 5 Aquarium Fish to Consider in 2025 for Beginners Introduction to Aquarium Fish Selection In the world of aquarium keeping, choosing the right fish is paramount, especially for beginners. The popularity of aquarium fish continues to grow, with 2025 introducing new enthusiasts to this vibrant hobby. Selecting the best aquarium fish not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of your aquatic oasis...
Exploring the Top 5 Most Colorful Fish to Discover in 2025 As aquarists look to brighten up their tanks in the upcoming year, the adventure of discovering vibrant fish species will take center stage. Colorful fish not only add a visually stunning element to any aquarium but also bring diverse personalities, behaviors, and unique habitats that can enchant fish enthusiasts. In...
Top 5 Effective Ways to Buy Angler Fish in 2025 Introduction to Buying Angler Fish In recent years, angler fish have gained popularity among seafood enthusiasts for their unique taste and culinary versatility. As we enter 2025, the demand for *angler fish* is expected to rise further, making it essential to understand the best ways to procure this delicacy. Whether you’re looking...
Effective Ways to Care for Pregnant Cherry Shrimp in 2025 Caring for pregnant cherry shrimp is an exciting and rewarding aspect of aquarium ownership, especially as more enthusiasts look to breed this vibrant and adaptable species. Cherry shrimp are not only popular for their beautiful colors and hardiness, but they also make excellent additions to community tanks and offer insight into...
Essential Guide to Betta Fish Accessories for Happy Aquariums Betta fish, known for their vibrant colors and unique personalities, require specific accessories to ensure they thrive in their aquariums. This guide focuses on essential betta fish accessories that not only enhance their environment but also promote their health and happiness. From proper filtration systems to decorative elements, every aspect plays a...